原题
1 | Given an input string (s) and a pattern (p), implement wildcard pattern matching with support for '?' and '*'. |
题意比较简单,就是 ? 表示任何单个字符,* 表示0到多个字符。类似于正则表达式
那么就可以看出来,
如果 s[i] == p[j] ,那就看 s[i+1…n], p[j+1…m] 是否匹配
如果 s[i] != p[j] && p[j] == ‘?’ 同上
如果 s[i] != p[j] && p[j] == ‘*’ 这种比较复杂
- 如果 * 表示空字符 则是否匹配取决于 s[i…n], p[j+1…m]是否匹配
- 如果 * 表示和s[i]相等的字符,则是否匹配取决于 s[i+1…n], p[j+1…m] 是否匹配
- 如果* 表示继续匹配s字符串之后的字符,则是否匹配取决于 s[i+1…n], p[j…m]
如果 s[i] != p[j] && p[j] != ‘?’ && p[j] != ‘*’ 则不匹配
通过以上的关系,就可以很轻松写出来递归,回溯的代码,但是这样是过不了的,当p中有很多*字符,那么肯定是超时的,效率很低
效率低是因为其中回溯的做法,没有记住中间状态,导致回溯过程中重复大量比较,浪费了时间。
如果用一个二维数组记住中间状态,就可以空间换时间,节约较多时间。
上面的四种情况,等价于 一下的等式
if s[i] == p[j] then dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j+1]
if s[i] != p[j] && p[j] == ‘?’ then 同上
if s[i] != p[j] && p[j] == ‘*’ then dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j+1] || dp[i+1][j] || dp[i][j+1]
if s[i] != p[j] && p[j] != ‘?’ && p[j] != ‘*’ then dp[i][j] = false
那么从等式就可以看出来前一个结果和回一个结果之间的依赖关系。
用题中给的例子,来画个图,
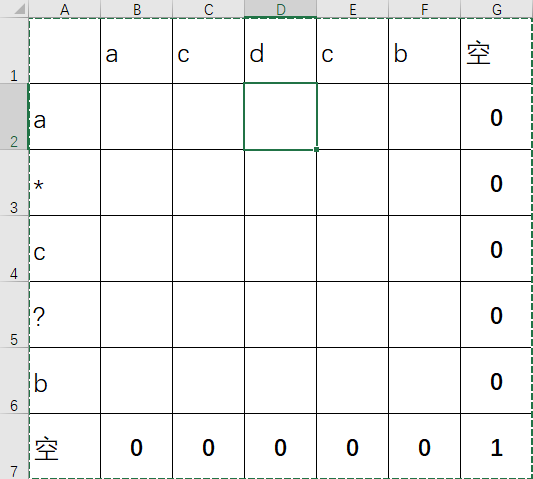
初始化的过程比较简单,其中需要注意的是3G的位置,由于匹配的是*,因此这个位置依赖于4G的位置
之后根据初始化的值和之前的依赖等式,就可以推导出来其他位置的值
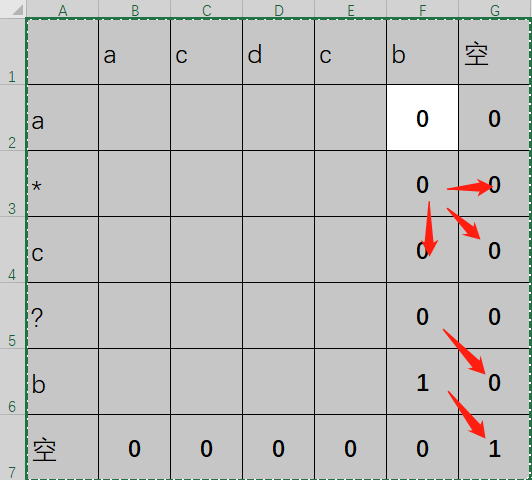
其中红色箭头就是依赖关系,还是比较清晰的,之后依次持续推算
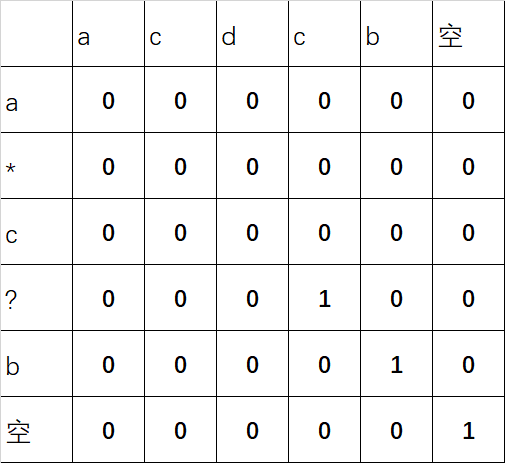
从最后图中可以看出dp[0][0] = false,所以不匹配,动态规划的做法记录了每一次计算的中间状态,省去了可能的大量重复计算,速度比较快。
代码
1 |
|